How does the OSPF cost work?
In this post, I will handle the OSPF cost (OSPF cost and auto-cost reference-bandwidth). Normally, I use the OSPF with default setting.
1. Pre-requisite.
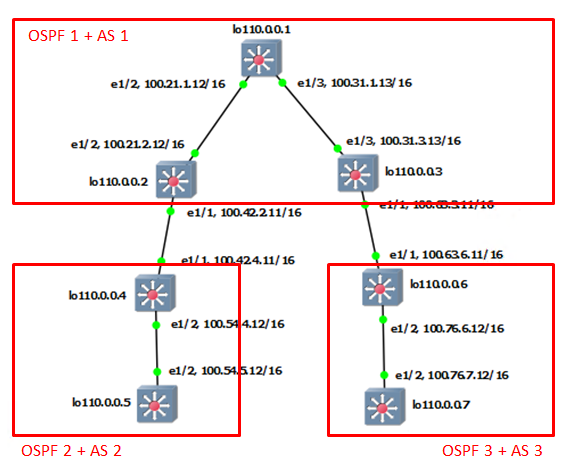
This is my environment to re-produce. I will write the simple configuration with default values.
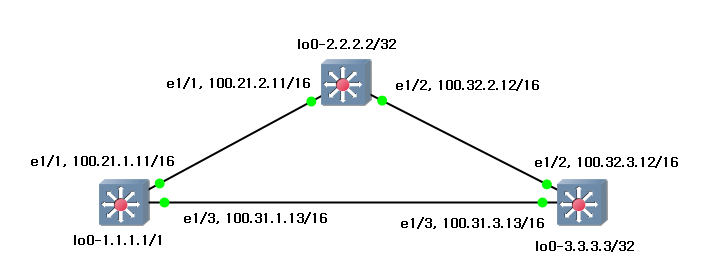
|
s1 (1.1.1.1/32) |
s2 (2.2.2.2/32) |
s3 (3.3.3.3/32) |
|
feature ospf interface Ethernet1/1 no switchport ip address 100.21.1.11/16 ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3 no switchport ip address 100.31.1.13/16 ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1/32 ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 |
feature ospf interface Ethernet1/1 no switchport ip address 100.21.2.11/16 ip router ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2 no switchport ip address 100.32.2.12/16 ip router ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2/32 ip router ospf 2 area 0.0.0.0
router ospf 2 router-id 2.2.2.2 |
feature ospf interface Ethernet1/2 no switchport ip address 100.32.3.12/16 ip router ospf 3 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3 no switchport ip address 100.31.3.13/16 ip router ospf 3 area 0.0.0.0 no shutdown
interface loopback0 ip address 3.3.3.3/32 ip router ospf 3 area 0.0.0.0
router ospf 3 router-id 3.3.3.3 |
2. Verify default status.
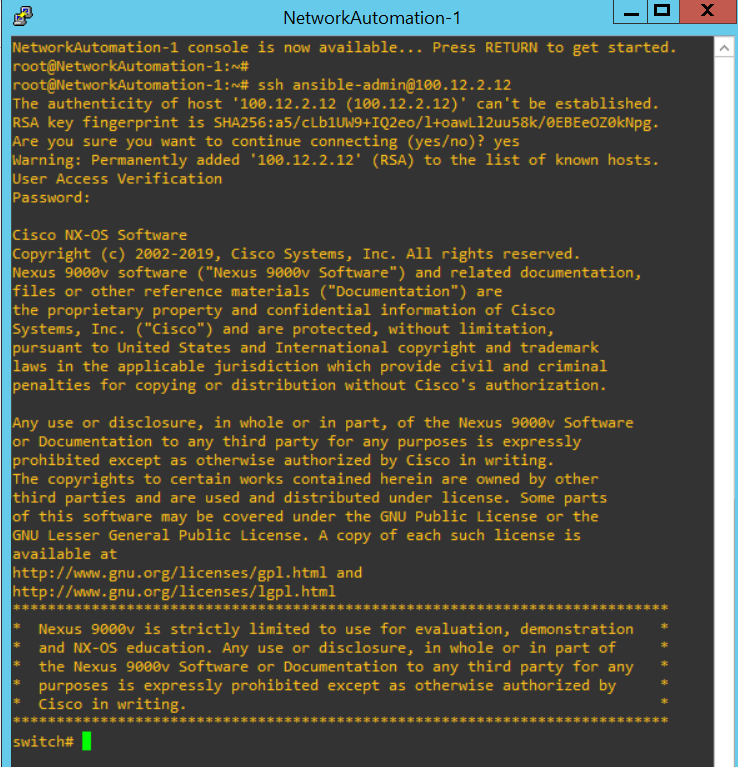
With default values, I can see the routing table over s1.
|
s1# show ip route 1.1.1.1/32, ubest/mbest: 2/0, attached *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:39:21, local *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:39:21, direct 2.2.2.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/41], 00:35:38, ospf-1, intra 3.3.3.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.31.3.13, Eth1/3, [110/41], 00:33:43, ospf-1, intra 100.21.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:36:44, direct 100.21.1.11/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:36:44, local 100.31.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:34:24, direct 100.31.1.13/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:34:24, local 100.32.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 2/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/80], 00:33:43, ospf-1, intra *via 100.31.3.13, Eth1/3, [110/80], 00:33:43, ospf-1, intra |
I can see the 2 kinds of values, [110/41] and [110/80]. The first value is the preference which is called as the administrative distance. In this instruction, there is the table list. In my case, I used the OSPF protocol which has 110 value as the default distance values.
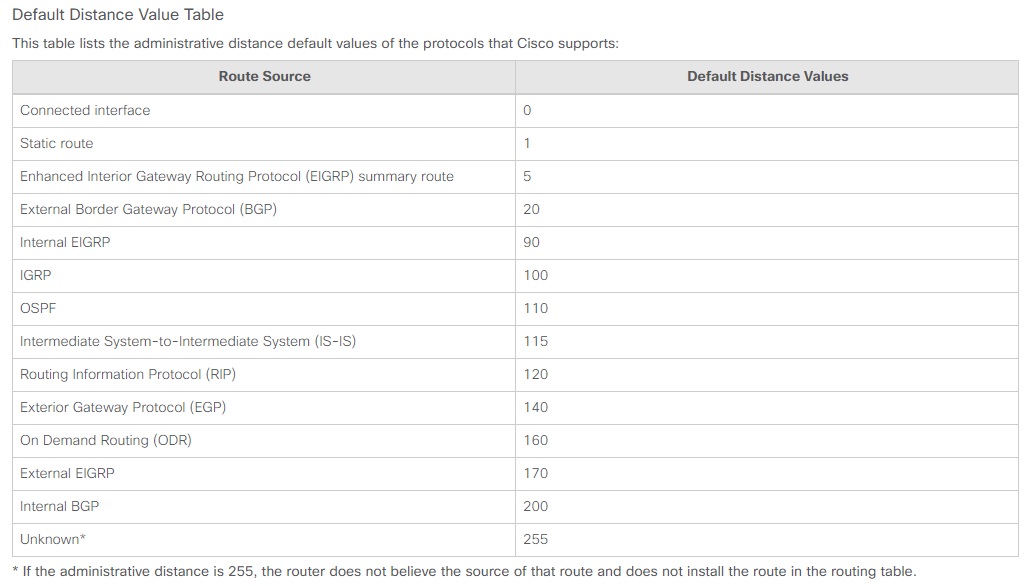
The second value is the metric which means the cost. The smaller value for the cost has higher priority.

From [110/41] and [110/80], "41" and "80" are the metric cost. Before calcuate these values, I need to understand the "auto-cost referece-bandwidth".
3. About auto-cost referece-bandwidth.
The cost is obtained by "auto-cost reference-bandwidth / interface bandwidth". In this instruction, it show how to configure this auto-cost reference-bandwidth. This is overview.
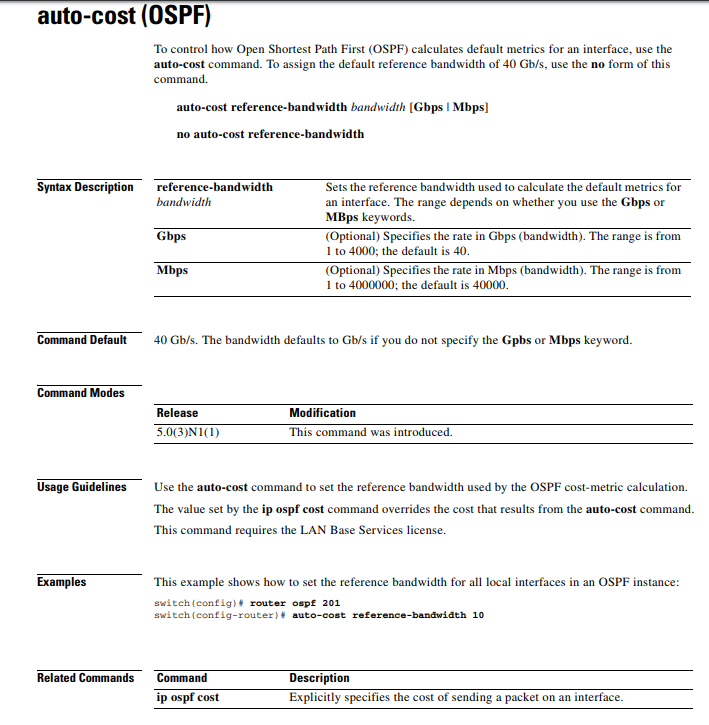
In my case, I used the Cisco Nexus image. Therefore, the default value is like below from this instruction.

I can verify this value with command, "show ip ospf". This is the sample from s1.
|
s1# show ip ospf Routing Process 1 with ID 1.1.1.1 VRF default Routing Process Instance Number 1 Stateful High Availability enabled Graceful-restart is configured Grace period: 60 state: Inactive Last graceful restart exit status: None Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA Administrative distance 110 Reference Bandwidth is 40000 Mbps SPF throttling delay time of 200.000 msecs, SPF throttling hold time of 1000.000 msecs, SPF throttling maximum wait time of 5000.000 msecs LSA throttling start time of 0.000 msecs, LSA throttling hold interval of 5000.000 msecs, LSA throttling maximum wait time of 5000.000 msecs Minimum LSA arrival 1000.000 msec LSA group pacing timer 10 secs Maximum paths to destination 8 Number of external LSAs 0, checksum sum 0 Number of opaque AS LSAs 0, checksum sum 0 Number of areas is 1, 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa Number of active areas is 1, 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa Install discard route for summarized external routes. Install discard route for summarized internal routes. Area BACKBONE(0.0.0.0) Area has existed for 02:52:56 Interfaces in this area: 3 Active interfaces: 3 Passive interfaces: 0 Loopback interfaces: 1 No authentication available SPF calculation has run 9 times Last SPF ran for 0.001811s Area ranges are Number of LSAs: 6, checksum sum 0x30590 |
Reference Bandwidth is 40000 Mbps. In s1, ethernet 1/1 and ethernet 1/3 have 1Gbps Bandwidth
|
s1# show inter et 1/1
s1# show inter et 1/3 |
Thus, 40000 Mbps / 1000 Mbps = 40. This is the cost. I can verify the value only with command "show ip ospf interface" also. The below is the sample from s1.
|
s1# show ip ospf interface Ethernet1/1 is up, line protocol is up IP address 100.21.1.11/16 Process ID 1 VRF default, area 0.0.0.0 Enabled by interface configuration State BDR, Network type BROADCAST, cost 40 Index 2, Transmit delay 1 sec, Router Priority 1 Designated Router ID: 2.2.2.2, address: 100.21.2.11 Backup Designated Router ID: 1.1.1.1, address: 100.21.1.11 1 Neighbors, flooding to 1, adjacent with 1 Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Hello timer due in 00:00:04 No authentication Number of opaque link LSAs: 0, checksum sum 0 Ethernet1/3 is up, line protocol is up IP address 100.31.1.13/16 Process ID 1 VRF default, area 0.0.0.0 Enabled by interface configuration State BDR, Network type BROADCAST, cost 40 Index 3, Transmit delay 1 sec, Router Priority 1 Designated Router ID: 3.3.3.3, address: 100.31.3.13 Backup Designated Router ID: 1.1.1.1, address: 100.31.1.13 1 Neighbors, flooding to 1, adjacent with 1 Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Hello timer due in 00:00:03 No authentication Number of opaque link LSAs: 0, checksum sum 0 loopback0 is up, line protocol is up IP address 1.1.1.1/32 Process ID 1 VRF default, area 0.0.0.0 Enabled by interface configuration State LOOPBACK, Network type LOOPBACK, cost 1 Index 1 |
I need to calculate these values. In this instruction, it show how to calculate and select the path.
4. Analysis the OSPF routing cost.
In s1 switch, [110/41] and [110/80] are the values as the cost.

I need to see more detail. "3.3.3.3" is the loopback interface. This IP address can be obtain with 2 path. "81" and "41" are the cost values. "41" is lower values. This is selected.
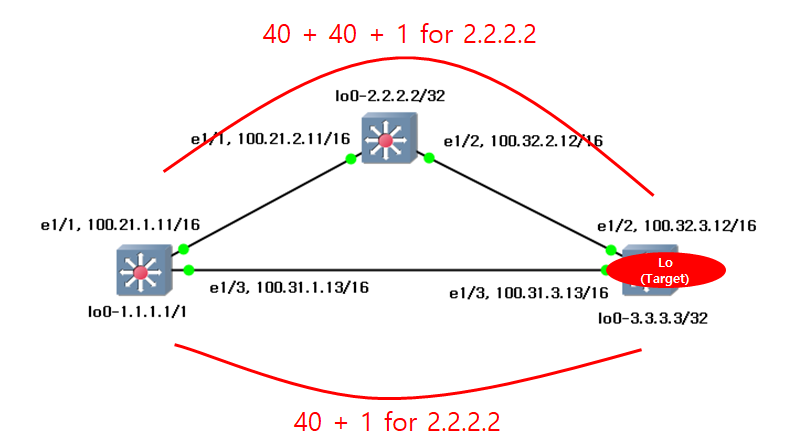
5. (Option 1) Adjust the Interface Bandwidth to change the path.
There are many method to determine the path. Most simple way is the change the interface bandwidth and speed. I change the interface bandwidth like below. Please read this instruction.
|
s1 (1.1.1.1/32) |
s3 (3.3.3.3/32) |
|
s1(config)# inter et 1/3 s1(config-if)# bandwidth 100000 |
s3(config)# inter et 1/3 s3(config-if)# bandwidth 100000 |
After then, I can check the interface bandwidth status
|
s1# show ip ospf inter et 1/3
s3# show ip ospf interface ethernet 1/3 |
Now, I can see the routing table changed like below.
|
s1# show ip route 1.1.1.1/32, ubest/mbest: 2/0, attached *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:07:12, local *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:07:12, direct 2.2.2.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/41], 00:06:11, ospf-1, intra 3.3.3.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/81], 00:05:29, ospf-1, intra 100.21.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:07:13, direct 100.21.1.11/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:07:13, local 100.31.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:07:12, direct 100.31.1.13/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:07:12, local 100.32.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/80], 00:05:29, ospf-1, intra |
6. (Option 2) Adjust the auto-cost reference bandwidth to change the path.
Auto-cost reference-bandwidth is the global parameter. Therefore, I change this value on s1 switch. There is no effect. Also there is no effect even if I change the value on s2 switch.

In this post, I will show how this value is changed.
| s1(config)# router ospf 1 s1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000 s1(config-router)# exit |
I can verify the ospf information
|
s1# show ip ospf Routing Process 1 with ID 1.1.1.1 VRF default Routing Process Instance Number 1 Stateful High Availability enabled Graceful-restart is configured Grace period: 60 state: Inactive Last graceful restart exit status: None Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA Administrative distance 110 Reference Bandwidth is 10000 Mbps |
Therefore, the routing table will be changed like below.
|
s1# show ip route 1.1.1.1/32, ubest/mbest: 2/0, attached *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:18:15, local *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:18:15, direct 2.2.2.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/11], 00:02:25, ospf-1, intra 3.3.3.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.31.3.13, Eth1/3, [110/11], 00:02:25, ospf-1, intra 100.21.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:18:16, direct 100.21.1.11/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:18:16, local 100.31.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:18:15, direct 100.31.1.13/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:18:15, local 100.32.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 2/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/50], 00:02:25, ospf-1, intra *via 100.31.3.13, Eth1/3, [110/50], 00:02:25, ospf-1, intra |
7. (Option 3) Adjust the ip ospf cost to change the path.
This is more effective way. However, I do not recommand this way. Because this can make complexity. In this instruction, it show how to configure. This configuration will be done on each interface.
| s1(config)# inter ethernet 1/3 s1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 100 s1(config-if)# exit |
This is the result on s1 switch
|
s1# show ip ospf interface ethernet 1/3 Ethernet1/3 is up, line protocol is up IP address 100.31.1.13/16 Process ID 1 VRF default, area 0.0.0.0 Enabled by interface configuration State BDR, Network type BROADCAST, cost 100 Index 3, Transmit delay 1 sec, Router Priority 1 Designated Router ID: 3.3.3.3, address: 100.31.3.13 Backup Designated Router ID: 1.1.1.1, address: 100.31.1.13 1 Neighbors, flooding to 1, adjacent with 1 Timer intervals: Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Hello timer due in 00:00:03 No authentication Number of opaque link LSAs: 0, checksum sum 0 |
Now, the path will be adjusted like below.
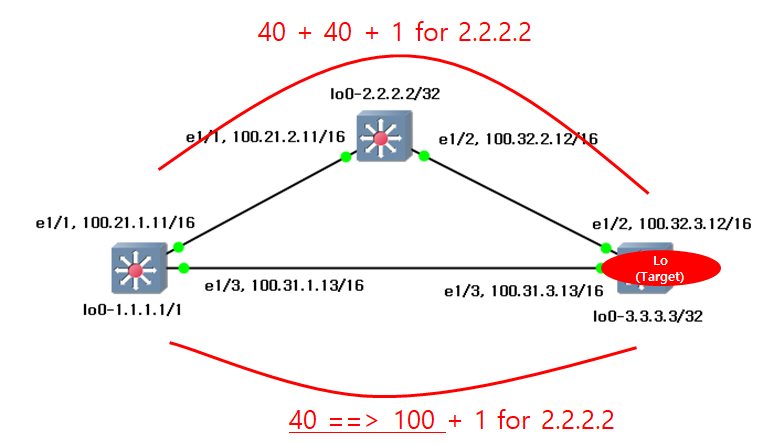
The routing table for s1 will be changed like below.
|
s1# show ip route 1.1.1.1/32, ubest/mbest: 2/0, attached *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:24:35, local *via 1.1.1.1, Lo0, [0/0], 00:24:35, direct 2.2.2.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/41], 00:04:23, ospf-1, intra 3.3.3.3/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/81], 00:01:52, ospf-1, intra 100.21.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:24:36, direct 100.21.1.11/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.21.1.11, Eth1/1, [0/0], 00:24:36, local 100.31.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:24:35, direct 100.31.1.13/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached *via 100.31.1.13, Eth1/3, [0/0], 00:24:35, local 100.32.0.0/16, ubest/mbest: 1/0 *via 100.21.2.11, Eth1/1, [110/80], 00:01:52, ospf-1, intra |
This is the OSPF cost concept.
Reference
[ 1 ] https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/15986-admin-distance.html
[ 2 ] http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=26129&seqNum=7
[ 5 ] https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/us/docs/2012/pdf/BRKARC-3472.pdf
[ 7 ] https://community.cisco.com/t5/networking-documents/how-to-configure-ospf-cost/ta-p/3133153
'Network Engineering > Basic Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OSPFv2 BR/BDR, Unnumbered Interface(Network Area, IP OSPF Area) Simple Concept. (0) | 2020.06.05 |
|---|---|
| How to ECMP load-balancing for CISCO? (ECMP Hashing) (0) | 2020.04.22 |
| How to work BGP synchronize and next hop self with Nexus? (0) | 2019.07.11 |
| What is basic BGP community concept? (0) | 2019.06.18 |
| How does the multicast (PIM sparse mode) work with MSDP? (0) | 2019.06.07 |